Microfinance Introduction:
Microfinance is a type of banking service provided to unemployed or low-income individuals or groups who otherwise would have no other access to financial services and it is also called Micro-credit.
The institutions working in the area of microfinance most often provide lending micro-loans which can range from as small as $150 to as large as $20,000, many banks offer additional services such as opening of deposit accounts such as current and savings accounts as well as micro insurance products, and some even provide financial and business education. The goal of microfinance is to ultimately give underprivileged people an opportunity to become self-reliant.
An Understanding to Microfinance:
Microfinance services are provided to unemployed or low-income individuals because most of those trapped in poverty, or who have limited financial resources and do not have enough income to do business with traditional financial institutions.
The people are excluded from banking services those who just earn as low as $2 a day and also try to save and borrow money to start some small business while to make payments on their debits, they also look for family, friends and even unconventional loan providers who charge high interest rates by taking the advantage of poor people having no access to normal banking system.
Microfinance allows people to take on reasonable small business loans safely, and in a manner that is consistent with ethical lending practices. Although they exist all around the world, the majority of microfinancing operations occur in developing nations, such as African countries and developing counties in Asia. Many microfinance institutions focus on helping women in particular.
Microfinancing organizations support a large number of activities that range from providing the basics, like bank checking and savings accounts to start up capital for small business entrepreneurs and educational programs that teach the principles of investing through their Financial Literacy Programs. These programs can focus on such skills as bookkeeping, cash-flow management, and technical or professional skills, like accounting.
Unlike typical financing situations, in which the lender is primarily concerned with the borrower having enough collateral to cover the loan, many microfinance organizations focus on helping entrepreneurs to succeed.
The Microfinance banks introduce their services to the urban and rural areas while conducting Program Introductions to create awareness regarding the microfinance services and also convey them the purpose of loan, its usage and interest rates.
The mobilized and educated persons who got information in Program introductions may apply for loans. Just as one would find at a traditional bank, a loan officer helps borrowers with applications, oversees the lending process, and approves loans. The typical loan, sometimes as little as $150, may not seem like much to some people in the developed world, but for many impoverished people, this figure often is enough to start a business or engage in other profitable activities.
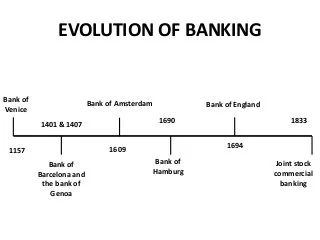
History of Microfinance
Microfinance is not a new idea as small operations have existed since the 18th century. The first occurrence of micro-lending is attributed to the Irish Loan Fund system, introduced by Jonathan Swift, which sought to improve conditions for impoverished Irish citizens. In its modern form, microfinancing became popular on a large scale in the 1970s.
The first Microfinance organization to receive recognition was the Grameen Bank, which was commenced its working in 1983 and its founder is Muhammad Younis in Bangladesh. In addition to providing loans to its clients, the Grameen Bank also suggests that its customers subscribe to its “16 Decisions”, a basic list of methods that the poor can improve their lives.
The “16 Decisions” touch upon a wide variety of subjects ranging from a request to stop the practice of issuing dowries upon a couple’s marriage, to keeping drinking water sanitary. In 2006, the Nobel Peace Prize was awarded to both Yunus and the Grameen Bank for their efforts in developing the microfinance system.
In Pakistan Microfinance Banks were introduced in 2000s when Government supported to establish a Microfinance bank through Microfinance ordinance and also helped by Asian Development bank and some other international institutions in providing the required funding. Currently, there are twelve Microfinance Banks are operating in Pakistan.
There are other microfinance operations around the world. Some larger organizations work closely with the world bank , while other smaller groups operate in different countries. Some organizations empower lenders to choose exactly who they want to support while categorizing borrowers with the set criteria such as level of poverty, geographic region and type of small business.
Others are very specifically targeted. There are organizations in Uganda, for example, that focus on providing women with the capital to undertake projects like growing eggplants and opening small cafés.
Some groups focus their efforts only on businesses whose goal is to improve the overall community through initiatives such as offering education, job training, and working toward a better environment.
Empowering women in particular, as many microfinance organizations do, may lead to more stability and prosperity for families.

The writer is having vast experience in Banking and Finance sector for over one and half decade, where during his period of work he has experienced different economic and development initiatives taken for the wellbeing of the public masses through the banking channel.
He has worked for the Microfinance banks which are offering community based services among the under developed segment of the society.
The major work done in Financial Inclusion where several hundreds of people were brought to Banking channel to improve their businesses.
The under served segment of society like woman were given the chances to change their lives through credit facilities to grow their home based businesses which is also an imitative of Women Empowerment.
The Writer has also worked against different social issues and highlighting them for positive change in the society through public awareness and their active involvement to reach to the solution.
This journey of empowering people is on going and is never lasting till the time last person remains underserved.