Introduction to Market economy:
A market economy is an economic system where two forces, known as supply and demand, direct the production of goods and services. Market economies are not controlled by a central authority like a government and are instead based on voluntary exchange.
In market economy the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers are unimpeded by price controls or restrictions on contract freedom.
Example of Market Economy:
If we can discuss the Market economy then the counties like the United States, England, and Japan are all examples of market economies.
1. No governmental control; goods and services are exchanged based on the market supply and demand as the government has no control over it.
2. The supply meets the demand; The products that are produced should be what the consumer wants. The consumer should be willing to pay for the product that they want.
3. Increased profitability; Firms should produce products that clients want, in doing that they will increase their profitability. By increasing their profitability, they will be able to utilize more workers to create more products and realize more income.
4. Innovation; Innovative companies will be able to produce products that consumers want. They will also be able to enhance the production process with new technology and equipment, making the product quality better and increasing customer satisfaction.
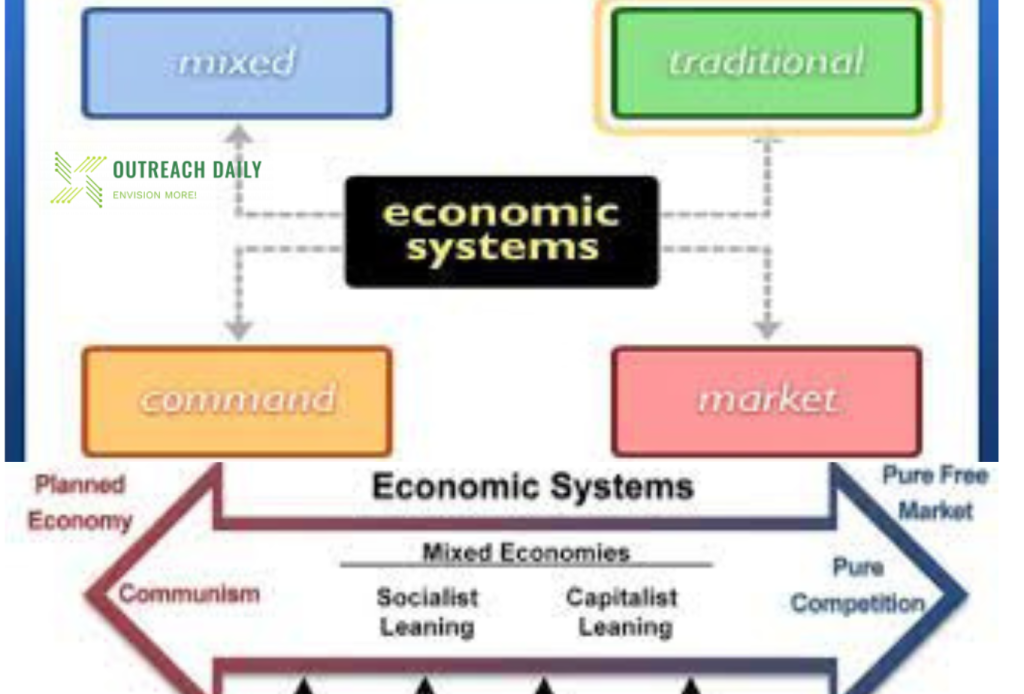
Market economies are characterized by:
- An economic system that relies on demand and supply.
- The quantity of the products that are produced is determined by the demand and supply.
Any Free Market economy exists?
In a free-market economy, the resources are owned by individuals, and the resource allocation is determined by these individuals, not the government. There are no recognized economies in the world that are 100% free-market economies.
Modern Market Economies:
The majority of the economies in the modern world are something between a pure market and a fully planned market economy. Industrialized nations usually make use of a mixed economy, they are often a free market that has some sort of government intervention. These economies could sometimes be classified as market economies because they allow the market to determine most of the activities the government will only intervene in when the market needs to be stabilized.
Government interventions include price-fixing, licensing, quotas, and industrial subsidies. Market economies are characterized by decentralized economic decisions that are made by buyers and sellers during everyday business.
Even though the market economy is a popular system, one should consider that how much government intervention is optimal for efficient economic operations.
Benefits of a Market Economy:
The benefits of a market economy include:
1. Resources are inevitably assigned to be consumed in the most effective way.
2. Consumers have a wide range of products to select from.
3. Innovation is exhilarated because of the profit purpose and self-interest of the market participants.
4. Competition ensures better quality products, hard-working labor, and hence overall high efficiency.
5. The economy offers a high chance of wealth due to its openness.
6. Products and services are manufactured based on consumers demands and how much they are willing to pay.
Drawbacks of a Market Economy:
The drawbacks of a market economy include;
1. Damage to the environment; economic activities can harm the environment; the wellbeing of the environment is not the focus of the market economy. Government regulations will have to mandate the safety of the environment.
2. Monopolies; technology breakthroughs can result in monopolies. Monopolies be likely to take advantage of consumers.
3. The inequality between income and wealth; if the return on capital is higher than the economic growth it will cause an income and wealth disparity. Disrupting the economy in the long run.
4. Automatic resource allocation; may result in specific ‘not very profitable’ yet vital sectors left off without enough resources which might have severe consequences over the long run.
5. Crises prone; for example, the profit motive may result in the adoption of automation and worker exploitation thereby dropping the disposable income and hence reducing consumption and plunging the economy into a recession
6. No government intervention; can lead to manufacturers charging the customers whatever fee they want.
7. Inequality; It faces inequality problems among the citizens.
Profit as a motive; As the government is in no control of production, profit is the only motive for the production of goods.
8. Poor working conditions; There might be poor working conditions as there is no government regulation in place.
9. Unemployment; Unemployment may rise as there is no government check in the market.
To conclude we can say that;
The benefits of a market economy include increased efficiency, production and innovation while the disadvantages of a market economy include monopolies, no government intervention, poor working conditions and unemployment. As the market economy has pros and cons due to liberalized things involved in it which are determined by the market itself instead of much interference from the centralized body or Government.

The writer is having vast experience in Banking and Finance sector for over one and half decade, where during his period of work he has experienced different economic and development initiatives taken for the wellbeing of the public masses through the banking channel.
He has worked for the Microfinance banks which are offering community based services among the under developed segment of the society.
The major work done in Financial Inclusion where several hundreds of people were brought to Banking channel to improve their businesses.
The under served segment of society like woman were given the chances to change their lives through credit facilities to grow their home based businesses which is also an imitative of Women Empowerment.
The Writer has also worked against different social issues and highlighting them for positive change in the society through public awareness and their active involvement to reach to the solution.
This journey of empowering people is on going and is never lasting till the time last person remains underserved.