Introduction to Islamic Banking:
Islamic banking is defined as banking system which is in consonance with the spirit, ethos and value system of Islam and governed by the principles laid down by Islamic Shariah. Interest free banking is a narrow concept denoting a number of banking instruments or operations which avoid interest.
Islamic banking, also referred to as Islamic finance or Shariah-compliant finance, refers to financial activities that observe to Shariah (Islamic law). Two essential principles of Islamic banking are the sharing of profit and loss and the prohibition of the collection and payment of interest by lenders and investors.
Practices of Islamic Banking:
Islamic banking is based on the beliefs of the Islamic faith as they relate to commercial transactions. The principles of Islamic banking are derived from the holy Quran–the central religious text of Islam. In Islamic banking, all transactions required to comply with Shariah, the legal code of Islam based on the teachings of the Holy Quran. The rules that govern commercial transactions in Islamic banking are referred to as fiqh al-muamalat.
Employees of institutions that abide by Islamic banking are trusted to not deviate from the basic principles of the holy Quran while they are conducting business. When guidance is required then Islamic bankers turn to learned scholars or use independent reasoning based on scholarship and customary practices.
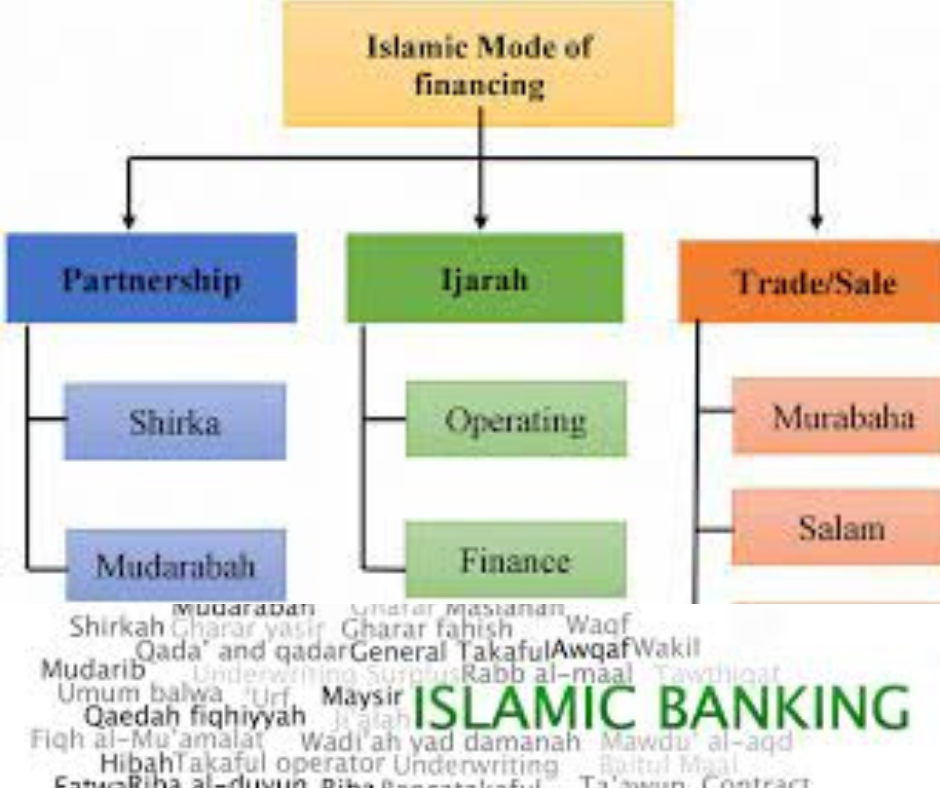
Modes of Islamic banking and finance:
Islamic Banking having trading, as Islam allows leasing of assets and getting rentals against the usufruct taken by the lessee. All such things/assets corpus of which is not consumed with their use can be leased out against fixed rentals. The ownership in leased assets remains with the lessor who assumes risks and gets rewards of his ownership.
Following are the main modes of Islamic banking and finance
1. MURABAHA
Literally it means a sale on mutually agreed profit. Technically, it is a contract of sale in which the seller declares his cost and profit. Islamic banks have adopted this as a mode of financing. As a financing technique, it involves a request by the client to the bank to purchase certain goods for him. The bank does that for a definite profit over the cost, which is stipulated in advance.
2. IJARAH
Ijarah is a contract of a known and proposed usufruct against a specified and lawful return or consideration for the service or return for the benefit proposed to be taken, or for the effort or work proposed to be expended. In other words, Ijarah or leasing is the transfer of usufruct for a consideration which is rent in case of hiring of assets or things and wage in case of hiring of persons.
3. IJARAH-WAL-IQTINA
A contract under which an Islamic bank provides equipment, building or other assets to the client against an agreed rental together with a unilateral undertaking by the bank or the client that at the end of the lease period, the ownership in the asset would be transferred to the lessee. The undertaking or the promise does not become an integral part of the lease contract to make it conditional. The rentals as well as the purchase price are fixed in such manner that the bank gets back its principal sum along with profit over the period of lease.
4. MUSAWAMAH
Musawamah is a general and regular kind of sale in which price of the commodity to be traded is bargained between seller and the buyer without any reference to the price paid or cost incurred by the former. Thus, it is different from Murabaha in respect of pricing formula. Unlike Murabaha, seller in Musawamah is not obliged to reveal his cost. Both the parties negotiate on the price. All other conditions relevant to Murabaha are valid for Musawamah as well. Musawamah can be used where the seller is not in a position to ascertain precisely the costs of commodities that he is offering to sell.
5. ISTISNA A
It is a contractual agreement for manufacturing goods and commodities, allowing cash payment in advance and future delivery or a future payment and future delivery. Istisna’a can be used for providing the facility of financing the manufacture or construction of houses, plants, projects and building of bridges, roads and highways.
6. BAI MUAJJAL
Literally it means a credit sale. Technically, it is a financing technique adopted by Islamic banks that takes the form of Murabaha Muajjal. It is a contract in which the bank earns a profit margin on his purchase price and allows the buyer to pay the price of the commodity at a future date in a lump sum or in installments. It has to expressly mention cost of the commodity and the margin of profit is mutually agreed. The price fixed for the commodity in such a transaction can be the same as the spot price or higher or lower than the spot price.
7. MUDARABAH
A form of partnership where one party provides the funds while the other provides expertise and management. The latter is referred to as the Mudarib. Any profits accrued are shared between the two parties on a pre-agreed basis, while loss is borne only by the provider of the capital.
8. MUSHARAKAH
Musharakah means a relationship established under a contract by the mutual consent of the parties for sharing of profits and losses in the joint business. It is an agreement under which the Islamic bank provides funds, which are mixed with the funds of the business enterprise and others. All providers of capital are entitled to participate in management, but not necessarily required to do so. The profit is distributed among the partners in pre-agreed ratios, while the loss is borne by each partner strictly in proportion to respective capital contributions.
9. BAI SALAM
Salam means a contract in which advance payment is made for goods to be delivered later on. The seller undertakes to supply some specific goods to the buyer at a future date in exchange of an advance price fully paid at the time of contract. It is necessary that the quality of the commodity intended to be purchased is fully specified leaving no ambiguity leading to dispute. The objects of this sale are goods and cannot be gold, silver or currencies. Barring this, Bai Salam covers almost everything, which is capable of being definitely described as to quantity, quality and workmanship.

The writer is having vast experience in Banking and Finance sector for over one and half decade, where during his period of work he has experienced different economic and development initiatives taken for the wellbeing of the public masses through the banking channel.
He has worked for the Microfinance banks which are offering community based services among the under developed segment of the society.
The major work done in Financial Inclusion where several hundreds of people were brought to Banking channel to improve their businesses.
The under served segment of society like woman were given the chances to change their lives through credit facilities to grow their home based businesses which is also an imitative of Women Empowerment.
The Writer has also worked against different social issues and highlighting them for positive change in the society through public awareness and their active involvement to reach to the solution.
This journey of empowering people is on going and is never lasting till the time last person remains underserved.